Keeping track of vaccinations remains a major challenge in the developing world, and even in many developed countries, paperwork gets lost, and parents forget whether their child is up to date. Now a group of Massachusetts Institute of Technology researchers has developed a novel way to address this problem: embedding the record directly into the skin.
Along with the vaccine, a child would be injected with a bit of dye that is invisible to the naked eye but easily seen with a special cell-phone filter, combined with an app that shines near-infrared light onto the skin. The dye would be expected to last up to five years, according to tests on pig and rat skin and human skin in a dish.
The system—which has not yet been tested in children—would provide quick and easy access to vaccination history, avoid the risk of clerical errors, and add little to the cost or risk of the procedure, according to the study, published Wednesday in Science Translational Medicine.
“Especially in developing countries where medical records may not be as complete or as accessible, there can be value in having medical information directly associated with a person,” says Mark Prausnitz, a bioengineering professor at the Georgia Institute of Technology, who was not involved in the new study. Such a system of recording medical information must be extremely discreet and acceptable to the person whose health information is being recorded and his or her family, he says. “This, I think, is a pretty interesting way to accomplish those goals.”
The research, conducted by M.I.T. bioengineers Robert Langer and Ana Jaklenec and their colleagues, uses a patch of tiny needles called microneedles to provide an effective vaccination without a teeth-clenching jab. Microneedles are embedded in a Band-Aid-like device that is placed on the skin; a skilled nurse or technician is not required. Vaccines delivered with microneedles also may not need to be refrigerated, reducing both the cost and difficulty of delivery, Langer and Jaklenec say.
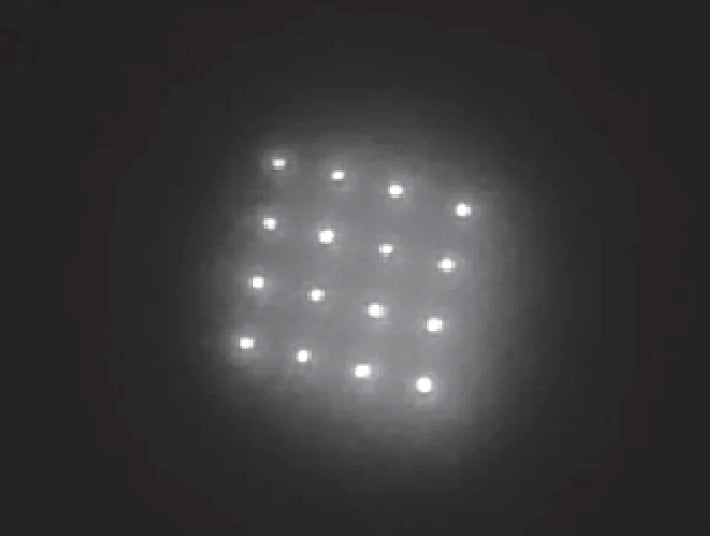
Delivering the dye required the researchers to find something that was safe and would last long enough to be useful. “That’s really the biggest challenge that we overcame in the project,” Jaklenec says, adding that the team tested a number of off-the-shelf dyes that could be used in the body but could not find any that endured when exposed to sunlight. The team ended up using a technology called quantum dots, tiny semiconducting crystals that reflect light and were originally developed to label cells during research. The dye has been shown to be safe in humans.
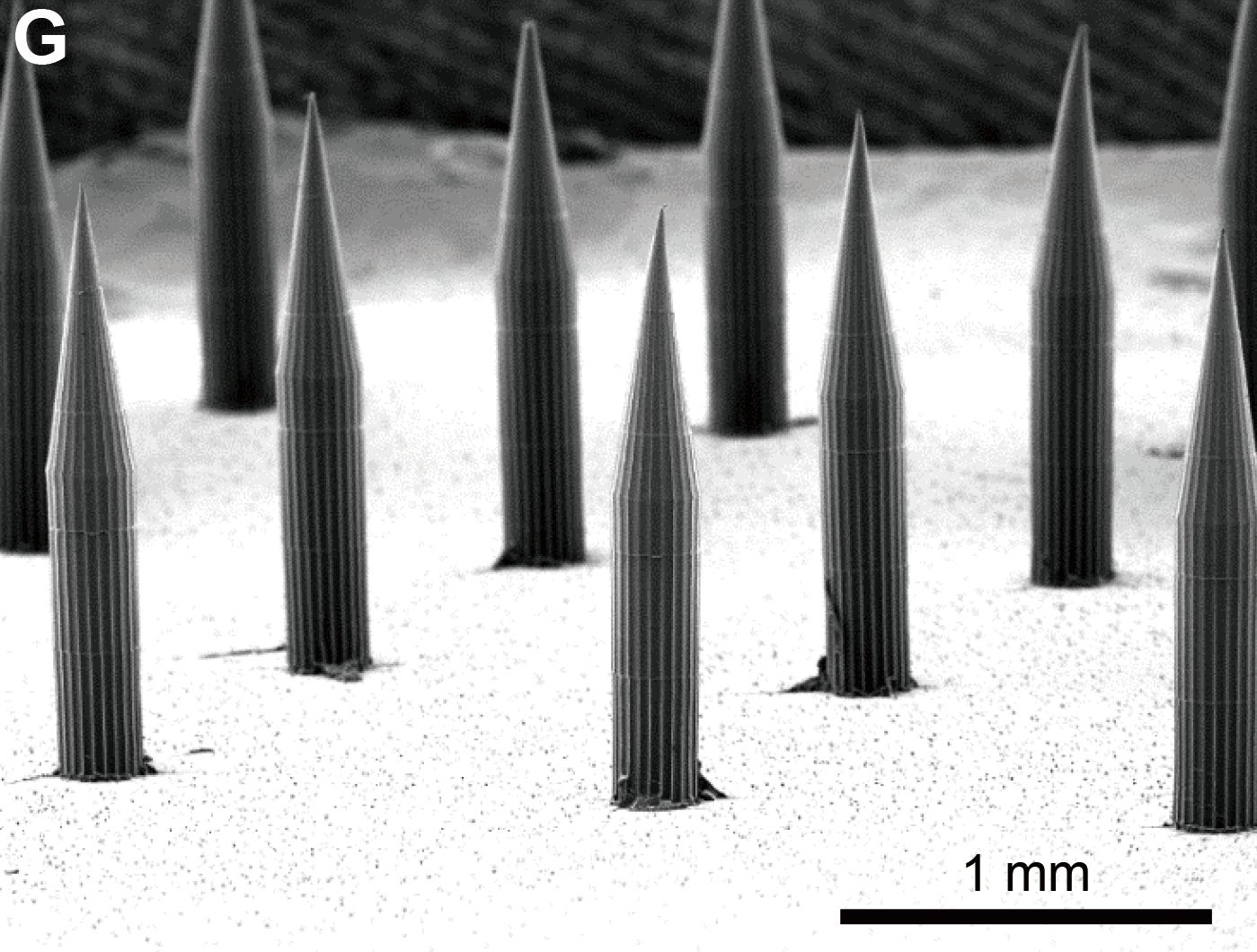
The approach raises some privacy concerns, says Prausnitz, who helped invent microneedle technology and directs Georgia Tech’s Center for Drug Design, Development and Delivery. “There may be other concerns that patients have about being ‘tattooed,’ carrying around personal medical information on their bodies or other aspects of this unfamiliar approach to storing medical records,” he says. “Different people and different cultures will probably feel differently about having an invisible medical tattoo.”
When people were still getting vaccinated for smallpox, which has since been eradicated worldwide, they got a visible scar on their arm from the shot that made it easy to identify who had been vaccinated and who had not, Jaklenec says. “But obviously, we didn’t want to give people a scar,” she says, noting that her team was looking for an identifier that would be invisible to the naked eye. The researchers also wanted to avoid technologies that would raise even more privacy concerns, such as iris scans and databases with names and identifiable data, she says.
The work was funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and came about because of a direct request from Microsoft founder and philanthropist Bill Gates himself, who has been supporting efforts to wipe out diseases such as polio and measles across the world, Jaklenec says. “If we don’t have good data, it’s really difficult to eradicate disease,” she says.
The researchers hope to add more detailed information to the dots, such as the date of vaccination. Along with them, the team eventually wants to inject sensors that could also potentially be used to track aspects of health such as insulin levels in diabetics, Jaklenec says.
This approach is likely to be one of many trying to solve the problem of storing individuals’ medical information, says Ruchit Nagar, a fourth-year student at Harvard Medical School, who also was not involved in the new study. He runs a company, called Khushi Baby, that is also trying to create a system for tracking such information, including vaccination history, in the developing world.
Working in the northern Indian state of Rajasthan, Nagar and his team have devised a necklace, resembling one worn locally, which compresses, encrypts and password protects medical information. The necklace uses the same technology as radio-frequency identification (RFID) chips—such as those employed in retail clothing or athletes’ race bibs—and provides health care workers access to a mother’s pregnancy history, her child’s growth chart and vaccination history, and suggestions on what vaccinations and other treatments may be needed, he says. But Nagar acknowledges the possible concerns all such technology poses. “Messaging and cultural appropriateness need to be considered,” he says.


