It’s been a rough year, especially on the health beat. The COVID pandemic continued to bulldoze its way through the population, causing surges in cases and related deaths. Somewhat forgotten viruses such as mpox, flu and RSV reared their head unexpectedly. And the U.S. Supreme Court overturned a nearly 50-year-old right to reproductive freedom established by Roe v. Wade.
But it wasn’t all bad news in 2022. In fact, biology and medicine saw exciting advances across fields as diverse as epidemiology, human evolution and artificial intelligence. Here are some of the discoveries that gave us hope for humanity and the future of human health.
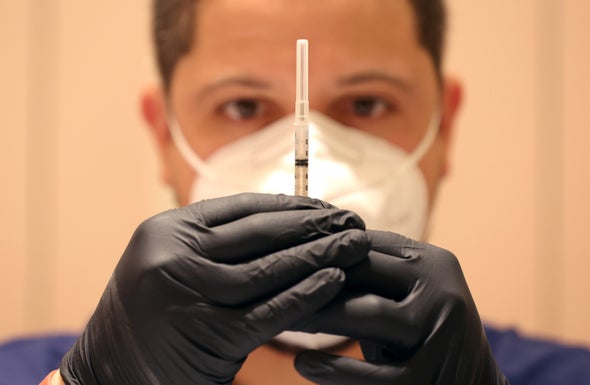
We Got Updated Versions of COVID Vaccines
The development of COVID vaccines within a year of the discovery of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes the disease, is undoubtedly one of the greatest medical achievements in recent memory. Two of the most effective vaccines, developed using mRNA technology, were proved to significantly protect against severe disease and death from SARS-CoV-2. But the virus continued to evolve, and newer variants began to find a way around human immune defenses. Fortunately, vaccine manufacturers developed new shots to target both the Omicron variant and the original strain. Early data suggest these “bivalent” vaccines effectively boost protection against the virus—all the more reason to make sure everyone in your family is up-to-date with their shots.
Discoveries in Human Evolution Won a Nobel Prize
This year’s Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Svante Pääbo for his discoveries involving the genetic relationships among our hominin ancestors. Pääbo, a Swedish geneticist and director of the Department of Evolutionary Genetics at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, pioneered methods for reconstructing ancient DNA. He and his colleagues sequenced the genome of Neandertals and discovered a new hominin species, Denisovans. The research led to the surprising revelation that early humans interbred with these now extinct species. These primeval trysts gave us traits that persist in some people today, including an ability to survive at high altitude and a vulnerability to infections such as COVID.
Scientists Revived Dead Pigs’ Organs
In a feat that sounds like something out of the pages of Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein, a team of scientists at Yale University developed a perfusion system that restored vitality to pigs’ organs after the animals had died. The system—known as OrganEx—pumped a mixture of blood and nutrient-rich fluid through each animal’s circulatory system. (The animals didn’t regain consciousness.) The technology holds the potential to keep more human organs alive longer for transplants.
Researchers Found Secrets in Our Poop
It sounds gross, but human waste contains a cornucopia of useful information for infectious disease scientists. Wastewater tracking systems enabled researchers to spot COVID cases and new SARS-CoV-2 variants in regions before they caused surges. By monitoring sewage, scientists also detected the virus that causes polio—a disease that has been declared eradicated in much of the world—in sewage systems in New York State and the U.K. This type of monitoring could also reveal spikes in opioid use or in levels of antibiotic-resistant microbes, scientists say.
We Learned That Indoor Air Quality Matters
Before the COVID pandemic, most of us probably didn’t give much thought to the air we breathe indoors. Over the past few years, though, it’s become clear that SARS-CoV-2 frequently spreads through airborne droplets, which can build up inside indoor spaces and make us sick. Fortunately, we can reduce that risk by ventilating buildings and filtering the air we breathe. And cleaner indoor air has other benefits: it reduces the risk of respiratory diseases in general, and it may even help us think more clearly.
AI Solved One of the Biggest Problems in Biology
One of the hardest problems for biologists is predicting the three-dimensional structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. But earlier this year an AI program built by the Google-owned company DeepMind, called AlphaFold, solved the 3-D structures of about 200 million proteins. These structures are already enabling scientists to unlock mysteries in biology, and they could help lead to new pharmaceutical drugs and more sustainable crops.