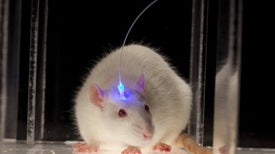
How to Make a Mouse Hallucinate
A real-time capture of brain-circuit activity shows how simple it is to change what an animal sees

A real-time capture of brain-circuit activity shows how simple it is to change what an animal sees

Brain cells that tick at regular intervals may coordinate neural activity like the conductor of an orchestra

Neuralink says it can robotically implant more than 3,000 flexible-polymer electrodes in a rat or monkey brain. The device is still a long way from routine human use, however

The ancient thinker saw limits to what natural science can tell us about ourselves
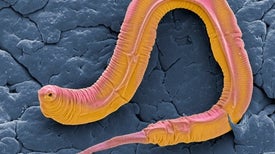
Genes in the humble C. elegans also turn up in autism, schizophrenia and other human disorders
A new study reveals surprising variations in the neural code

The new discipline of network neuroscience yields a picture of how mental activity arises from carefully orchestrated interactions among different brain areas
Neural processing centers repeat recent sequences of events to lay down new memories used for abstract thought

By switching fruit flies' sensory neurons on and off with light, scientists were able to create the sensation of sweet or bitter tastes. Christopher Intagliata reports.
A study in mice shows improved cognitive performance when these bursting signals move around memory circuits

A new study used machine learning to show how “all mutations are not created equal”

A new study in mice reveals why consuming a beverage is usually pleasurable but is not always enough to quench thirst
Preterm babies who listened to music in the neonatal intensive care unit had brain activity that more closely resembled that of full-term babies. Christopher Intagliata reports.

Artists, novelists, actors and directors excel at tapping into “imagination” circuits

New study suggests that early screening may benefit some children

A prototype detects whom you are listening to and amplifies only that speaker’s voice; a potential solution to the “cocktail party problem”

Blocking an immune-related molecule lodged in blood vessels stops memory loss

A new study adds to growing evidence that immune system dysfunction and altered gut microbes may contribute to the development of eating disorders
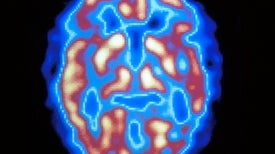
A new algorithm accurately identified more than 90 percent of people who would advance to an Alzheimer’s diagnosis in about six years

Experiments in humans and animals have started to identify how violent behaviors begin in the brain
Support science journalism.

Thanks for reading Scientific American. Knowledge awaits.
Already a subscriber? Sign in.
Thanks for reading Scientific American. Create your free account or Sign in to continue.
Create Account