
New EPA Rules Would Slash Power Plant Emissions
The EPA has announced new draft rules that would require power plants that burn fossil fuels to capture 90 percent of their climate-warming emissions

The EPA has announced new draft rules that would require power plants that burn fossil fuels to capture 90 percent of their climate-warming emissions

Aggressive restrictions will affect carbon, smog and soot emissions from compact cars all the way up to long-haul trucks

The greenhouse gas intensity of offshore oil and gas production in the Gulf of Mexico could be twice as much as government estimates
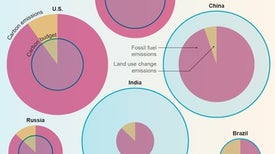
Some countries have used up far more of the world’s carbon budget—the amount we can emit and still avoid more extreme climate disruption—than others

The U.S. is in a better place to reach its climate goals after the passage of the Inflation Reduction Act and the bipartisan infrastructure bill, but the implementation of pollution rules and the outcome of the 2024 election could pose major hurdles...

Scientists say countries need to cut emissions far deeper to prevent catastrophic warming. That fact will hang over delegates when they meet later this year at the annual U.N. climate talks...

The IPCC’s latest climate assessment says the world must cut greenhouse gas emissions by 60 percent by 2035, but the U.S. is already behind on a less ambitious target...

The Nord Stream pipeline explosions happened in a dumping ground for chemical warfare, but other contaminants proved most toxic to marine life

Texas education officials adopted changes to internal guidance on textbooks that could steer schools to buy books that misinform students about global warming

A coalition of environmental and Indigenous groups is suing the Biden administration over the approval of the Willow oil- and gas-drilling project in Alaska, arguing the government failed to consider the climate risks, as well as harm to wildlife and subsistence hunting...

India is at an energy crossroads: if it chooses fossil fuels, it could undermine global climate targets

Oil and gas facilities will soon be charged for releasing methane, but technologies to capture the potent greenhouse gas are still relatively new and untested

Scientists working for the oil giant Exxon in the 1970s and 1980s estimated temperature increases with remarkable accuracy. Those findings could now be used as evidence in climate litigation...

Though renewable energy surpassed coal generation for the first time in 60 years, causing U.S. power emissions to decline, emissions from buildings and transportation went up in 2022

Extreme heat has provided some relief from Europe’s punishing energy crunch. Trouble looms, though, as it continues to seek alternative energy sources

Increasing demand for natural gas and oil has offset emissions reductions associated with coal and pushed U.S. energy emissions higher for a second consecutive year

Sustainable aviation fuel is poised for exponential growth thanks to increased investment and policy support, according to industry officials

Higher fossil energy prices and concerns about energy supply disruptions are driving the acceleration of wind, solar and other renewables, the International Energy Agency says

Wind, solar and hydropower will generate more than 20 percent of the power supply

New funding programs announced at COP27 are helping poor countries transition away from fossil fuels, but the money isn’t going to places without energy
Support science journalism.

Thanks for reading Scientific American. Knowledge awaits.
Already a subscriber? Sign in.
Thanks for reading Scientific American. Create your free account or Sign in to continue.
Create Account